Adding different barcode types (including QR codes) to your PDFs, whether for retail, pharmacy, or industrial purposes is easy with PDF Ink. Since PDF Ink, when used with WordPress, allows you to accept some user input before your PDF file is downloaded, you can even include that data in your barcode! Completely customized barcodes added on-the-fly to your PDFs, as they are downloaded… that’s pretty cool!
We get it – the documentation on TCPDF barcoding with all those PHP arguments is bewildering. If you are using TCPDF and need assistance incorporating barcodes into your application, get in touch — we can help you customize 1D and 2D barcodes to your PDFs whether you are using PDF Ink or not. That said, PDF Ink is designed to make it really easy to add barcodes to your PDF files!
1D vs 2D Barcodes
What’s the difference between a 1D and a 2D barcode? It depends on whether data is read in one direction, or two.

On the left, a 1D barcode. Data is read horizontally via bars of differing width. Data is not read vertically on a 1D barcode. On the right, a 2D barcode; data is read horizontally and vertically.
You may be familiar with the 2D barcode, as QR codes have become a popular means of distributing branding and marketing via smartphones and other readers. Adding a barcode to your PDF is not only great way to make your PDFs look “cool” and add function, but it can also give the end user the impression that you take your data seriously. Flex!
Your custom barcodes can be any size, any color, printed anywhere on the PDF page. You can have one or more completely different barcodes printed on each page. The barcodes are configurable using TCPDF parameters, included in the settings panel. No coding necessary! If you are using SetaPDF-Stamper and want barcodes, great! SetaPDF-Stamper will add a barcode — created by TCPDF — to your PDF. Again, no coding necessary!
Here’s a more detailed description about creating very customized barcode shapes on PDFs using TCPDF via PDF Ink.
TCPDF Barcode List
Here are the barcode types recognized by TCPDF. They are separated out into 1d and 2d lists below.
- CODE 39. Also called Alpha39, Code 3 of 9, Code 3/9, Type 39, USS Code 39, or USD-3. International standard ISO/IEC 16388) (C39)
- CODE 39 with checksum (C39+)
- CODE 39 extended (C39E)
- CODE 39 extended with checksum (C39E+)
- CODE 93 (USS-93, Canada Post)
- Standard 2 of 5 (S25)
- Standard 2 of 5 + (S25+)
- Interleaved 2 of 5 (I25)
- Interleaved 2 of 5 + (I25+)
- CODE 128. International Standard ISO/IEC 15417. (C128)
- CODE 128 A
- CODE 128 B
- CODE 128 C
- EAN 2 (GTIN). 2-Digits UPC-Based Extension. European Article Number. Magazines. (EAN2)
- EAN 5 (GTIN). 5-Digits UPC-Based Extension. Books. (EAN5)
- EAN 8 (GTIN). International Standard ISO/IEC 15420 (EAN8)
- EAN 13 (GTIN). International Standard ISO/IEC 15420 (EAN13), can encode ISBN
- Universal Product Code (UPC-A)
- UPC-E
- MSI. Modified Plessey. Warehouse use.
- MSI+
- POSTNET Old USPS barcode
- PLANET Old USPS barcode, retired 2013
- Royal Mail 4-state Customer Code – Customer Bar Code (RMS4CC)
- Klant index – Customer index – PostNL (KIX)
- Intelligent Mail Barcode – Onecode – USPS-B-3200 – United States Postal Service (IMB)
- Pre-processed Intelligent Mail Barcode, using only F,A,D,T letters (IMBPRE)
- CODABAR. Library use.
- CODE 11. Telecommunications.
- PHARMACODE. Pharmaceutical use
- PHARMACODE TWO-TRACKS (PHARMA2T)
- DATAMATRIX
- PDF417 International standard: ISO/IEC 15438. (PDF417 + a[aspect ratio (width/height)],e[error correction level (0-8)],t[total number of macro segments],s[macro segment index (0-99998)],f[file ID],o0[File Name (text)],o1[Segment Count (numeric)],o2[Time Stamp (numeric)],o3[Sender (text)],o4[Addressee (text)],o5[File Size (numeric)],o6[Checksum (numeric)])
- QRCODE. International Standard: ISO/IEC 18004
- QRCODE,L. Low error correction (7%).
- QRCODE,M. Medium error correction (15%).
- QRCODE,Q. Quartile error correction (25%)
- QRCODE,H. High error correction (30%)
- RAW. Comma-separated list of array rows
- RAW2. Array rows are surrounded by square parenthesis.
- TEST. Test matrix.
List of 1D Barcodes
CODE 39, CODE 39+, CODE 39 extended, C39 Extended+, CODE 93, Standard 2 of 5, Standard 2 of 5+, Interleaved 2 of 5, Interleaved 2 of 5+, CODE 128, CODE 128 A, CODE 128 B, CODE 128 C, EAN 2, EAN 5, EAN 8, EAN 13, UPC-A, UPC-E, MSI, MSI+, POSTNET, PLANET, RMS4CC, Klant Index, IMB, IMBPRE, CODABAR, CODE 11, PHARMACODE, PHARMACODE Two Tracks
You can see examples of these 1D barcodes on the TCPDF website.
List of 2D Barcodes
TCPDF supports the following 2D barcode types: DATAMATRIX, PDF417 (a,e,t,s,f,o0,o1,o2,o3,o4,o5,o6), QRCODE, QRCODE L, QRCODE M, QRCODE Q, QRCODE H, RAW, RAW2, and TEST.
You can see examples of these 2D barcodes on the TCPDF website.
Barcode Settings
In order to add barcodes to your PDFs, you must be using the TCPDF writing library. The barcode feature is road-mapped for SetaPDF-Stamper, but not FPDF.
Barcodes replace placement content saved in the settings. There are up to four native placements in the Frontend and Sandbox settings. So naturally, you can easily have up to four barcodes on each page. If you need more, it’s easy to add more placements using a couple lines of PHP.
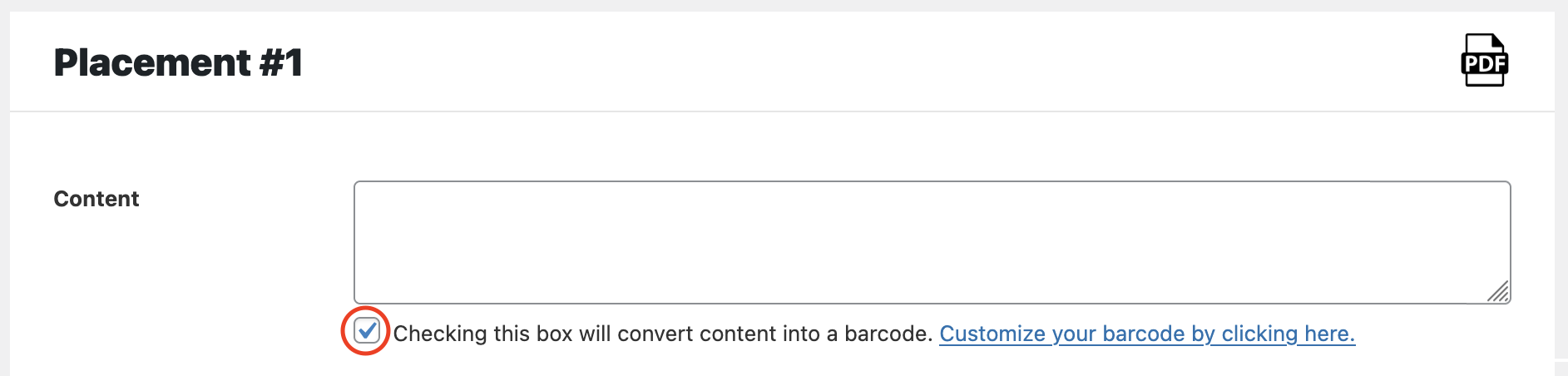
Under each placement content field is a checkbox (circled in red in the image below):
1D Settings
1D and 2D settings are slightly different, so different dialogue boxes will open depending on which barcode type you choose. We’ll share an example to illustrate common 1D settings.
1D Barcode Settings by Example
Checking the box will convert content into a barcode. So if you want to barcode an address, enter the address into the Content field or maybe use a postal address Magic Tag. We used [POSTCODE][ORDERNUMBER], which should print out 9020110361 for our test customer’s order 10361. (Yes, the customer is in Beverly Hills.)
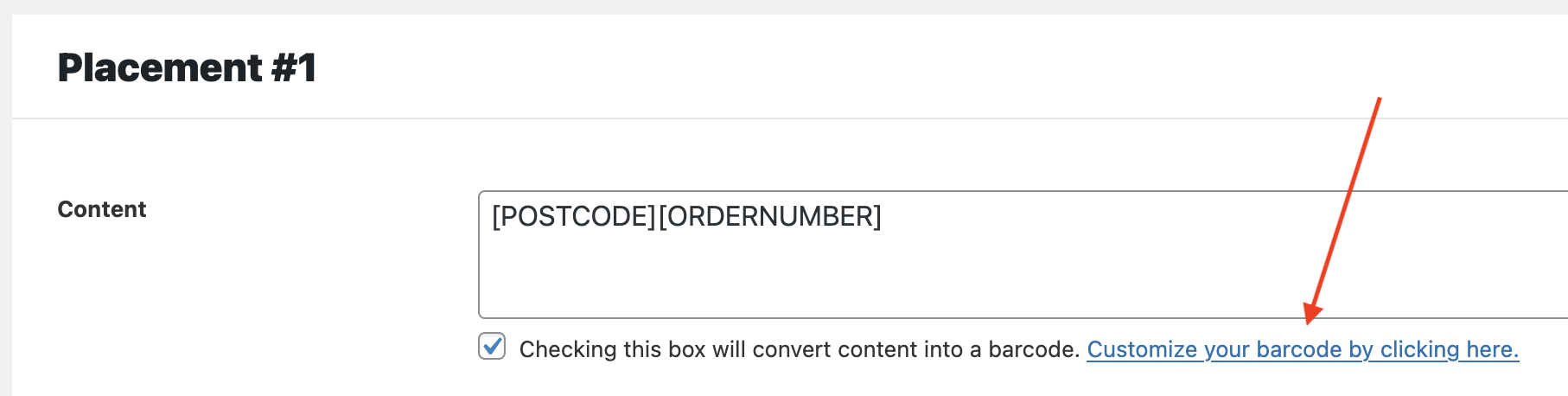
To customize the barcode (borders, padding, colors) click the “Customize your barcode” link and a popup will show:
Start by choosing a “Barcode type”
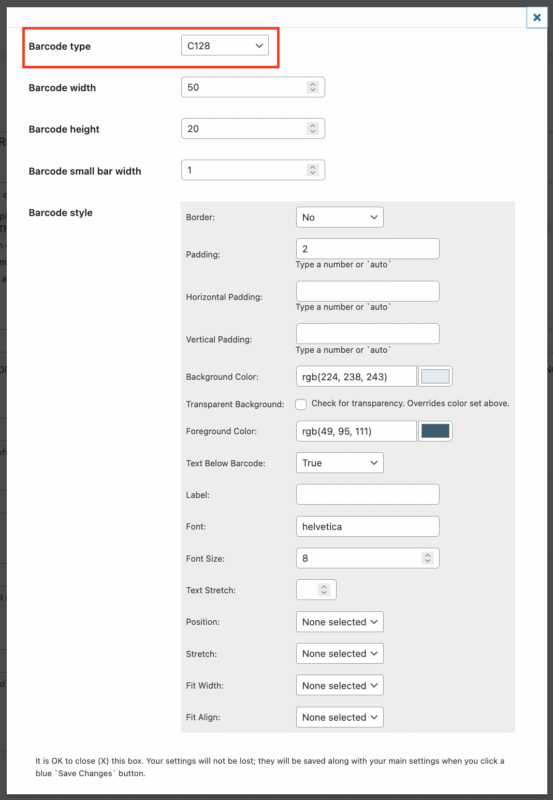
In our example we are setting up a C128 barcode. C128 is a very widely-used linear barcode format to represent numeric or alphanumeric strings in the shipping and packaging industries. Keep in mind some other barcode types only allow numeric strings, and some recognize more characters than others. For instance, if you try to print letters (a-z|A-Z) using the EAN or UPC type, you will receive an error.
Barcode Width & Height
Width and height settings dictate how much real estate the barcode will take on the page. Measurements are in points (1 point = 1/72 of an inch). Any borders or padding will occur inside this real estate, making the barcode smaller than the width and height.
Barcode Small Bar Width
This is the width of the smallest bar in millimeters. If left blank, the default is 0.4mm.
If width and height are set, and stretch is not set to false, barcode small bar width settings will not take effect.
Above you can see we have decided the barcode will be 5cm width x 2cm height on the page, 2mm padding with dark green bars and a light blue background. Learn more about 1D barcode style (the settings in the light grey box). Once you fill out the settings, X out the popup box and save them on the main screen.
We used the [ZIPCODE][ORDERNUMBER] magic tags to populate the numbers 9021010361. Since “Text Below Barcode” is set to true, those numbers will print below the bars in Helvetica font. If you only want to see the bars, do not set “Text Below Barcode” to true.
The content looks like this, placed on the lower right corner of the page:
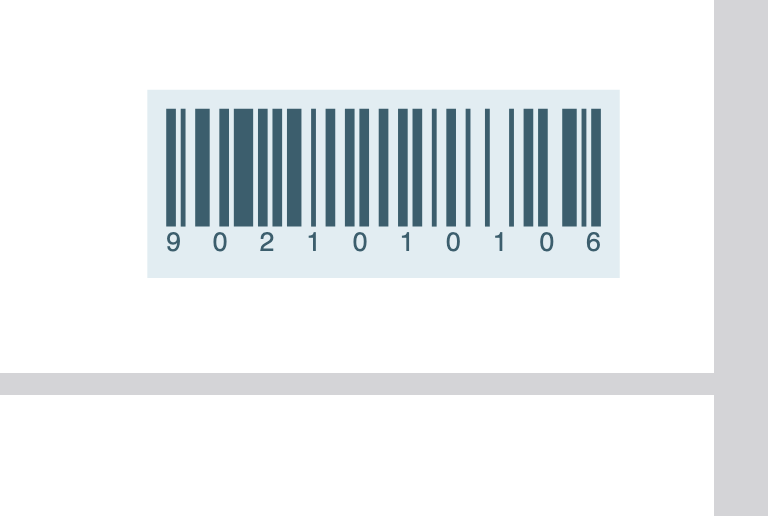

The example above is for a custom C128 (1D) barcode. This barcode would print differently for every customer, based on their zip code and the order number. Obviously this is a weird example of C128 use, but highlights how creativity can be used, too!
1D Barcode Style Parameters:
The following parameters would be used as an array if you were using TCPDF programmatically, but PDF Ink spares you this task. The barcode array are easy settings fields in PDF Ink (look for the inputs in a light grey box). Below each aspect of the “1D Barcode Style” is explained a bit:
| border (boolean) | If true, prints a border. Default false. |
| padding (int) | Padding to leave around the barcode in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding). All padding happens inside the bounds set by the barcode width and height. |
| hpadding (int) | Horizontal padding in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding) |
| vpadding (int) | Vertical padding in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding) |
| fgcolor (array) | Color array for bars and text |
| bgcolor (mixed) | Color array for background (set to false for transparent) |
| text (boolean) | If true prints text below the barcode. Default false. |
| label (string) | Override the default text label (printed below barcode) |
| font (string) | Font name for text, e.g. helvetica or times |
| fontsize (int) | Numeric font size for text |
| stretchtext (int) | 0 = disabled; 1 = horizontal scaling only if necessary; 2 = forced horizontal scaling; 3 = character spacing only if necessary; 4 = forced character spacing. |
| position (string) | Horizontal position of the containing barcode cell on the page: L = left margin; C = center; R = right margin. |
| align (string) | Horizontal position of the barcode on the containing rectangle: L = left; C = center; R = right. |
| stretch (boolean) | If true stretch the barcode to best fit the available width, otherwise uses $xres resolution for a single bar. If fitwidth is true, stretch becomes false. |
| fitwidth (boolean) | If true reduce the width to fit the barcode width + padding. When this option is enabled the ‘stretch’ option is automatically disabled. |
| cellfitalign (string) | This option works only when ‘fitwidth’ is true and ‘position’ is unset or empty. Set the horizontal position of the containing barcode cell inside the specified rectangle: L = left; C = center; R = right. |
2D Settings
Barcode Width & Height
2D barcodes share the width and height settings with 1D barcodes (learn more above). That makes sense, right? Any type of barcode can have a width and height set.
Barcode Alignment
You can ignore this… or read on to learn why. In TCPDF, the $align parameter tells the PDF writer where to put the pointer after it is done printing the QR code. Examples: If “Top” (T) is set, then trailing text or content would continue along the top right edge of the QR code (assuming RTL). If “Next” (N) is set, a new line would be started below the QR code. This setting is omitted from PDF Ink because each placement resets the pointer, making an alignment setting moot.
Barcode Distort
If checked, TCPDF distorts the barcode shape to fit width and height. Otherwise preserves aspect ratio set by width and height.
2D Barcode Style Parameters
Below each aspect of the “2D Barcode Style” is explained a bit:
| border (boolean) | If true, prints a border |
| padding (int) | Padding to leave around the barcode in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding) |
| hpadding (int) | Horizontal padding in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding) |
| vpadding (int) | Vertical padding in user units (set to ‘auto’ for automatic padding) |
| module_width (int) | Width of a single module in points |
| module_height (int) | Height of a single module in points |
| fgcolor (array) | Color array for bars and text |
| bgcolor (array) | Color array for background or false for transparent |
| position (string) | Barcode position on the page: L = left margin; C = center; R = right margin; S = stretch |
2D Barcode Examples
Coming very soon!